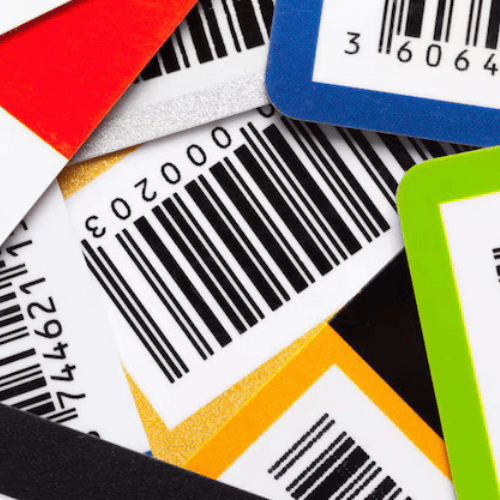
In the dynamic retail world, barcodes are pivotal in simplifying operations, maximizing inventory management, and enhancing the overall customer experience. With the advancement of technologies, different barcode types serve diverse retail purposes. In this blog, we examine the top barcodes scanner in retail, their uses, and why they are important to contemporary businesses.
- UPC (Universal Product Code)
UPC barcodes are most commonly used in retail, especially in North America. UPC barcodes are 12-digit numeric codes that make it easy for retailers to track products.
Why is UPC Important?
- Standardized for global retail use
- Enables quick and accurate scanning
- Reduces checkout time and human errors
- EAN (European Article Number)
EAN barcodes are the same as UPC but are utilized primarily outside of North America. They exist in two forms: EAN-8 (for smaller products) and EAN-13 (for regular products).
Advantages of EAN Barcodes
- Internationally accepted, allowing smooth international transactions
- Utilized by most supermarkets and online retailers
- Enables automated stock management
- QR Codes (Quick Response Codes)
QR codes are increasingly used in retailing because they can hold large volumes of data. QR codes are not restricted to scanning from a single direction, unlike standard barcodes.
Benefit of QR Codes in Retail
- May contain website links, product information, and offers
- Increases customer interaction by mobile scanning
- Suits digital payments and loyalty schemes
- Code 128
Code 128 is a high-density barcode, primarily used in inventory and logistics. It encodes all 128 ASCII characters, which means it is extremely versatile.
Why Use Code 128?
- Small and efficient to manage warehouses
- Offers detailed product data
- Prevents inventory mismatches
- Data Matrix Codes
Data Matrix barcodes are 2D barcodes that contain significant amounts of data in a minimal area. They are used most often in the healthcare and retail packaging industries.
Key Benefits of Data Matrix Codes
- Great for monitoring small retail products
- error-proof and extremely resistant
- Supports direct part marking (DPM)
- GS1 DataBar
GS1 DataBar is a more recent barcode format applied primarily to fresh produce and small retail products. It offers extra product data like expiration dates.
Why use GS1 DataBar?
- Handles variable-weight products
- Improves food safety by making them traceable
- Aids retailers to meet regulatory requirements
Selecting the Appropriate Barcode for Your Retail Business
Choosing the best barcode requires your business use, type of product, and scanning technology. Here’s a shortcut guide:
- For ordinary retail goods: UPC or EAN
- For inventory management and logistics: Code 128 or GS1 DataBar
- For customer interaction: QR codes
- For compact and high data density storage: Data Matrix codes
The Future of Barcodes in Retail
With technological advancements, barcode systems are becoming intelligent. The use of RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and AI-based analytics is revolutionizing retail operations. Retailers who implement these technologies can automate processes, minimize losses, and improve customer experiences.
Conclusion
Barcodes are a vital aspect of retailing. From classic UPCs to cutting-edge QR and Data Matrix codes, each barcode has its function in streamlining efficiency and customer satisfaction. Retailers seeking to remain competitive need to invest in the proper barcode scanner in order to optimize their business.
Do you need barcode solutions for your retail business? Zahabi offers high-quality barcode systems to assist retailers in optimizing their operations. Get in touch with us today to learn more about our barcode solutions!